Subsystem Export¶
A key feature of Lynx is interoperability with the Python Control Systems Library, referred to here as python-control or control.
Python-control stores system parameters as NumPy arrays, so they can easily be translated to block parameters by directly referencing the variables:
import control
import lynx
# Create a system in python-control
s = control.tf('s')
sys = control.ss((s + 1) / s^2)
# Use the parameters for the Lynx block
diagram = lynx.Diagram()
diagram.add_block('state_space', 'plant', A=sys.A, B=sys.B, C=sys.C, D=sys.D)
Perhaps a more powerful feature is the capability to go the other direction and export python-control objects from Lynx diagrams. This enables all of the simulation, analysis, and design tools in python-control without complex block diagram algebra.
For instance, the "cascaded" template provides a pre-built diagram structure with 16 blocks including plant models, inner and outer control loops, and noise and disturbance inputs.
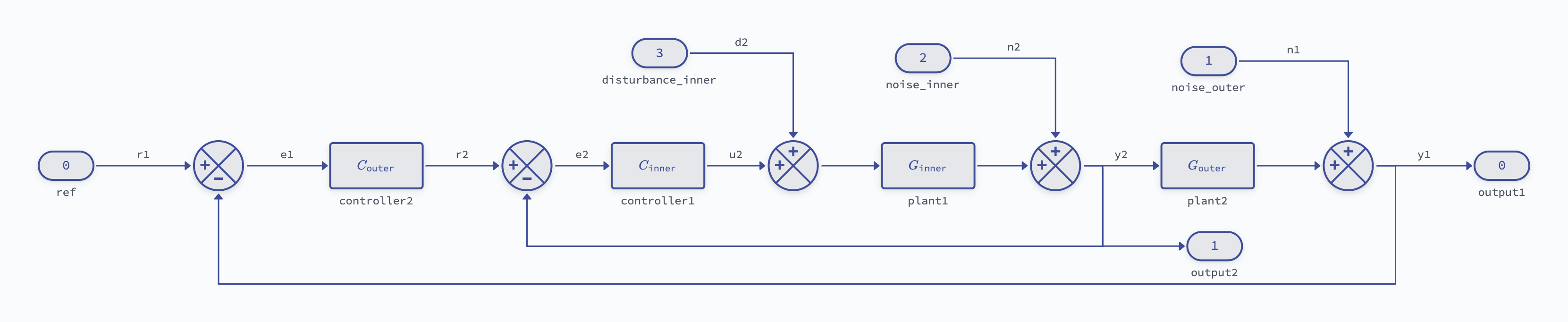
Since the important signals have all been labeled, it’s trivial to extract any internal subsystem in either a state-space or transfer function representation:
diagram = lynx.Diagram.from_template("cascaded")
# Transfer function from inner loop disturbance (d2) to outer loop output (y1)
subsys_tf = diagram.get_tf("d2", "y1")
# Same subsystem in state-space form
subsys_ss = diagram.get_tf("d2", "y1")
Signal References for Export¶
When you export a subsystem with diagram.get_ss(from_signal, to_signal) or diagram.get_tf(from_signal, to_signal), Lynx needs to identify which signals to use. Signal references follow a 3-tier priority system:
1. IOMarker Labels (Highest Priority)¶
Use the label parameter from InputMarker or OutputMarker blocks:
diagram.add_block('io_marker', 'ref_marker', marker_type='input', label='r')
diagram.add_block('io_marker', 'out_marker', marker_type='output', label='y')
# Export using IOMarker labels (recommended)
sys = diagram.get_tf('r', 'y')
Best practice: Use IOMarker labels for all system boundaries and subsystem extraction.
2. Connection Labels (Medium Priority)¶
Reference labeled connections between blocks:
diagram.add_connection('error_conn', 'sum', 'out', 'controller', 'in',
label='error')
# Export using connection label
sys = diagram.get_ss('r', 'error')
Use case: Extracting internal signals without adding extra IOMarker blocks.
3. Block.Port Notation (Lowest Priority)¶
Explicit reference using block_label.output_port format:
# Export using block label + port
sys = diagram.get_ss('controller.out', 'plant.out')
Important:
Must use block label (not internal block ID)
Must reference output ports only (signals are outputs, not inputs)
Requires explicit
.outsuffix
Signal Resolution Example¶
# All three signals are valid for export:
# - 'ref' (IOMarker label - highest priority)
# - 'e' (connection label)
# - 'controller.out' (block.port notation)
# Get transfer function from reference to error
sys_re = diagram.get_tf('ref', 'e')
# Get transfer function from error to plant output
sys_ey = diagram.get_tf('e', 'plant.out')
# Full closed-loop transfer function
sys_ry = diagram.get_tf('ref', 'output')